Main features:
- Preprocessing of inputs
- Hierarchical architecture with local receptive fields
- Weight-sharing/equality-constraints
- Standard approaches: MA, AR and ARMA models. These are all linear and therefore unsuitable for most practical problems.
- Neural network approaches:
- tapped delay lines - sensitive only to a fixed number of steps
back in time, but allow for precise computation to be made over
that limited window
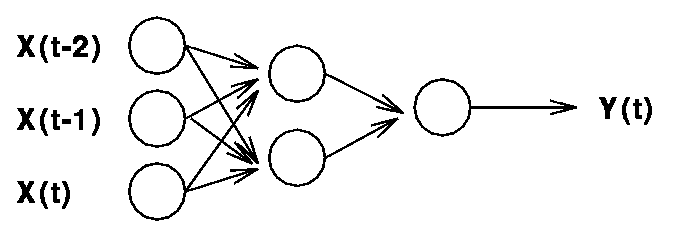
- recurrent networks - sensitive arbitrarily far back in time,
but info is blurred in time
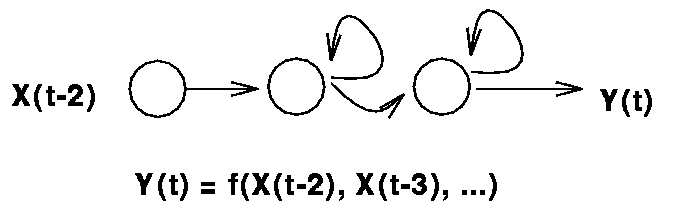
- tapped delay lines - sensitive only to a fixed number of steps
back in time, but allow for precise computation to be made over
that limited window
- Applications:
- Predicting geyser eruptions (covered in assignment 2)
- Predicting breakouts in steel casting.
Ghahramani and Hinton used a version of the Mixture of Competing Experts arhitecture, a modular arhcitecture that can divide up a problem into different regimes and separately model them.
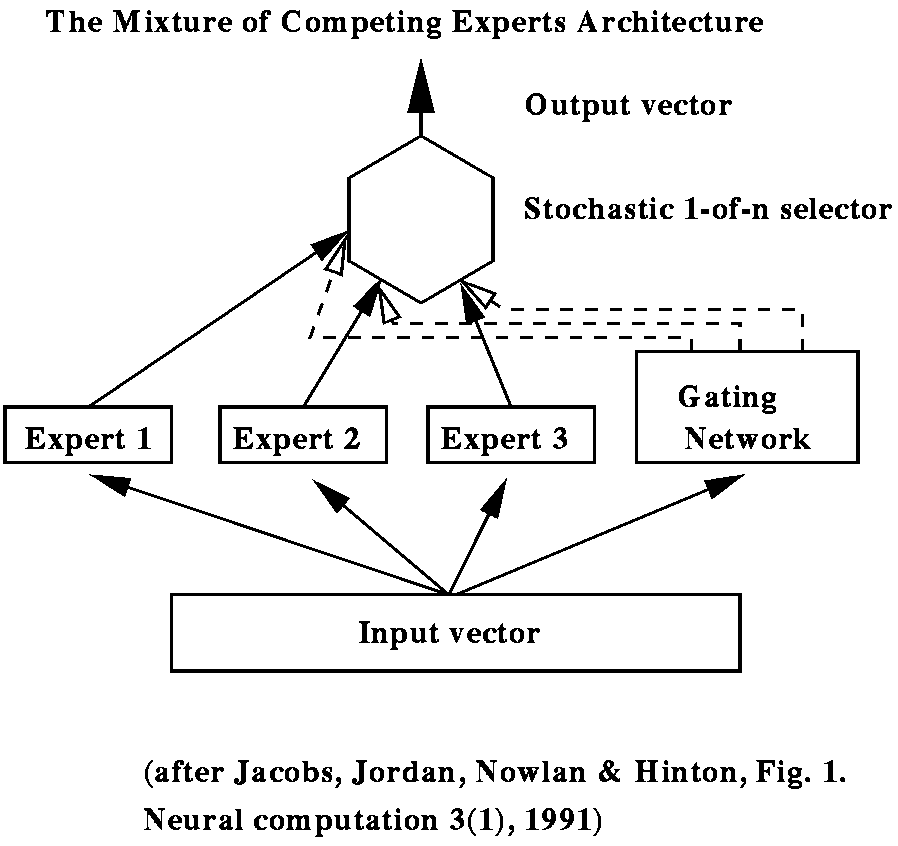
Each expert network was linear but used recurrent connections (a linear Kalman filter). The nonlinear gating network computed coefficients that were used to combine the experts' outputs into a single global prediction. The network was thereby able to handle very different regimes of the input, such as startup conditions versus normal operating conditions. A probabilistic interpretation of the outputs allowed the network to indicate its own certainty that it could account for each piece of data, and thereby detect abnormal operating conditions.
Major features & design issues:
- Simple feed-forward architecture - potential drawbacks?
- Output representation for steering controls
- Generalization to new road conditions - use diverse training set, and train on translated images to achieve translation-invariance
- Output reliability monitoring: use of a secondary auto-encoder network for input reconstruction
- Nettalk - converting text to speech
- 'Radar' the talking robot (demo),
using speech recognition chip by Sensory Inc.
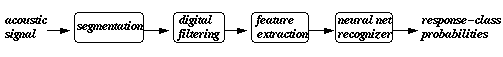 Figure 1. Mozer's architecture for speaker-independent recognition.
Figure 1. Mozer's architecture for speaker-independent recognition.
"Figure 1: the basic processing stages that occur when an acoustic signal is presented for speaker-independent recognition: segmentation (where the utterance begins and ends in the continuous input stream), digital filtering for time normalization and acoustic feature extraction, and a neural network recognizer.
A huge amount of work goes into the preprocessing and data collection
"Speaker-independent recognition with a vocabulary of a dozen alternatives achieves recognition accuracies greater than 95% in actual usage" (Mozer, 1996).
- Glove-talk (video): an illustration of the use of
neural networks in adaptive interfaces (no reading, but see Adaptive
Mixtures of Local Experts paper for background)
Major features:- Learns to map from hand gestures, which are input via a dataglove, to speech, which is output via a synthesizer.
- A neural network learns the mapping, using vowel and consonant networks
- the above two networks use radial basis functions (RBF's) for hidden units. The RBFs allow the hidden layer to develop "local features" that represent a small region of the high-dimensional input space. This tends to make training faster and is good for interpolation across the vowel space. That is, a wide range of input parameters (including intermediary values not previously trained on) can be mapped to a single vowel sound.
- A third "V/C network" decides which of the first two nets is appropriate, as in the mixture of competing experts architecture.
Key points:
- Equivalence between Principal Componenets Analysis (PCA) and multi-layer auto-encoder networks in the 3-layer case: The mapping learned by the hidden layer can be shown to be equivalent to Principal Components Analysis (PCA), a well known technique for dimension reduction which projects the data onto the subspace containing maximum variance in the data. PCA selects the dimensions corresponding to the eigenvectors of the data covariance matrix having the largest eigenvalues.
- Demo: encoding 2-d images of "Gaussian blobs", compressed through a bottleneck of hidden units: emergence of value-codes versus variable-codes, depending on compression rate.
![[Previous]](prevsec.gif)
![[Parent]](parntsec.gif)
![[Next]](nextsec.gif)